In a highly digitized and regulated environment, financial institutions are constantly challenged to maintain a consistent brand image, enhance the customer experience, and comply with regulatory demands. By automatically monitoring sent and received emails and text messages, financial institutions can ensure regulatory compliance, identify areas for improvement in communication, and safeguard their brand reputation. In this article, we’ll explore how message auditing has become crucial in the financial world, along with brand governance, regulatory compliance, and email archiving, to help institutions successfully navigate the digital landscape. 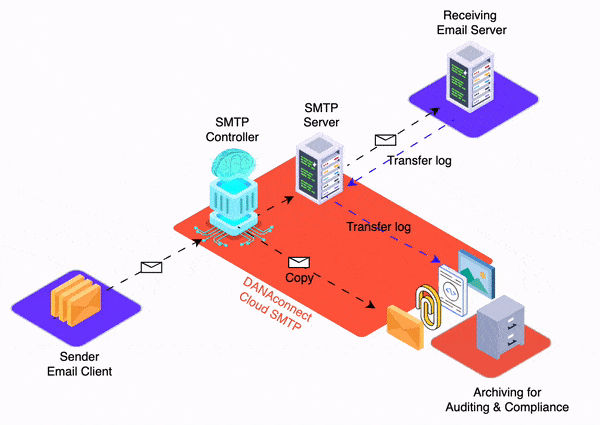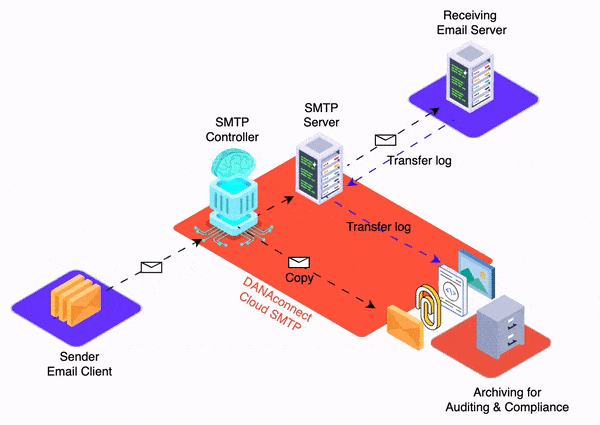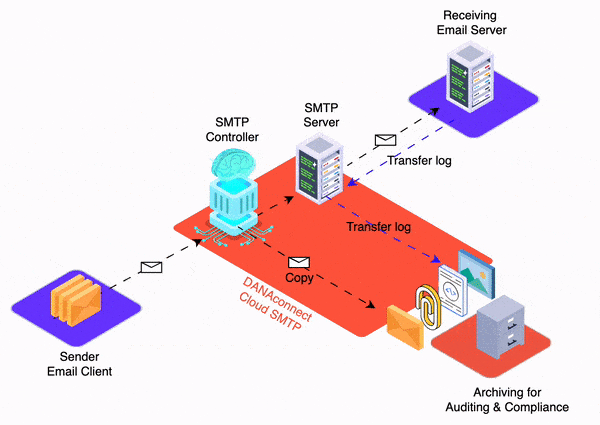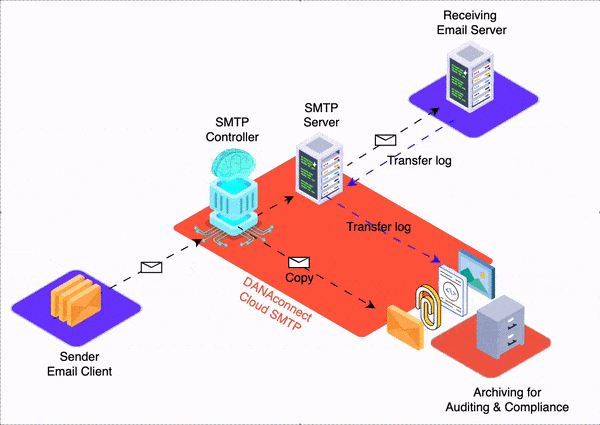
The Importance of Audit Capabilities over Digital Communications
Regular auditing of emails and text messages allows companies to identify and fix potential compliance issues before they become regulatory violations. The audit also provides valuable insight into how customer communication is taking place, which can help improve the effectiveness of communication and marketing strategies.
Message Auditing: Protecting Reputation and Ensuring Compliance
First, message auditing has become an indispensable tool for monitoring and controlling customer interactions. Message auditing, which involves systematic examination of sent email and text messages, helps financial institutions ensure regulatory compliance, improve customer experience, and protect brand reputation.
For example, in a regulated environment such as finance, message audits can reveal whether a company is complying with its legal communication obligations. Additionally, by analyzing customer communications, companies can identify and correct potential problems, such as unclear or misleading communication. Finally, in the event of a dispute with a customer, message auditing can provide invaluable evidence.
Regulatory Compliance: The Importance of Message Auditing
Regulations in the financial sector often stipulate that institutions must keep accurate records of all communications with clients. This can include everything from online transactions and alerts, to email correspondence and text messages.
Message audits can play a crucial role in complying with these regulations. By systematically reviewing and storing all electronic communications, financial institutions can demonstrate to regulators that they are complying with their legal obligations. Also, in the event of an investigation or legal dispute, having a communications file can be invaluable.
Support to the Legal Department and Savings in Litigation
The emails often contain critical information that can serve as evidence in legal disputes. Archived emails can help organizations respond effectively to legal requests for information, such as eDiscovery warrants, reducing potential penalties and litigation costs.
In the context of litigation, the parties involved may request the production of documents relevant to the case. This may include emails that may contain relevant or incriminating information. Having a well-organized and searchable email archiving system can simplify the eDiscovery process and reduce associated costs.
Email Archiving: Preserving the Past, Protecting the Future
Finally, email archiving is an essential practice for all financial institutions. Email archiving not only helps institutions meet record retention obligations, it also protects against data loss and facilitates information retrieval.
Best practices for email archiving include implementing an automated archiving system, email classification, indexing and labeling, and regular data recovery testing. Additionally, financial institutions must ensure that their email archiving practices are in line with local and global regulations.
What should be stored in the email trace history for auditing?
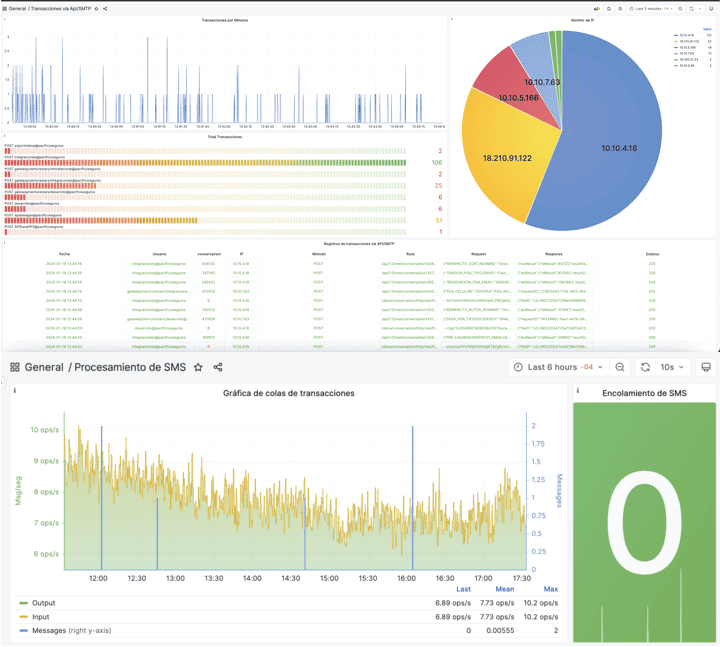
Email trace history is a detailed record of activity related to an email from its creation to its delivery and further handling. This traceability is essential for message auditing, as it allows financial institutions to track and analyze all stages of an email’s lifecycle and ensure that security and regulatory requirements are met. Some of the items that are stored in the email trail history for auditing include:
- Sender and recipient data: The email address of the sender and all recipients of the message, including those in the “CC” and “BCC” (blind carbon copy) fields, are recorded.
- Send date and time: The exact moment the message was sent from the sender’s server is recorded.
- Date and time of receipt: The exact moment the message was received on the recipient’s server is recorded.
- Message ID and Tracking: Each message has a unique identifier that allows specific tracking of that email throughout the delivery and handling process.
- Delivery route: The route the message took from the sender’s server to the recipient’s server is recorded, including details about any intermediary servers it may have passed through.
- Opening and reading record: Some email tracking solutions can provide information on whether the email was opened and read by the recipient.
- Link click log: In the case of messages containing links, it can be recorded if the recipient clicked on any of them.
- Record of downloads and attachments: If the message contains attachments, it can be recorded if they were downloaded by the recipient.
- Log of errors or delivery problems: In case delivery problems occur, information about the reason for the failure, such as incorrect addresses or blocking by the recipient’s server, must be logged along with the response code of the incoming server.
- Storage of the Body of the Email Content in Original Format: The body of the email content is stored in its original format, which includes any text formatting, images, hyperlinks, and formatting styles used by the sender. This ensures that the integrity of the original message is maintained and that any relevant information is not altered during the archiving process.
- Storage of Attachments in Original Format: Attachments sent or received with email are also stored in their original format. This means that documents, images, multimedia files and any other type of file are preserved without modification to guarantee their authenticity and fidelity to the original content sent or received by the sender.
All of this information should be stored in a detailed registry that allows financial institutions to audit and verify the authenticity, integrity, and compliance of electronic communications. This traceability is especially important in regulated environments, as it allows institutions to demonstrate that they are complying with legal and regulatory obligations when it comes to communication with clients. Furthermore, email trace history can also be valuable in situations of legal disputes or investigations, providing clear and verifiable evidence of customer interactions.
Are you looking for an email archiving solution that will help you cut costs by up to 80%? Contact us.
Top 5 Misconceptions About Corporate Email Archiving
Enterprise-level email archiving is a critical practice to ensure security, compliance, and efficient information management. However, it is also common to find some misconceptions about this practice. Here are five of the top mass email archiving misconceptions at the enterprise level:
- Email archiving is for legal compliance only: A common belief is that email archiving is only necessary to comply with legal regulations and retention requirements. While compliance is an important reason for archiving, it is also crucial to facilitate quick information search and retrieval, protect against data loss, and improve email handling efficiency.
- Email archiving is expensive and complicated: Some organizations may think that implementing an archiving system is expensive and complicated. However, with technological advances and the cloud archiving solutions, (like DANAconnect) are now more accessible and profitable than ever. Additionally, complexity can be reduced by choosing archiving solutions that are intuitive and easy to use.
- All email must be permanently archived: A common mistake is to archive all email indefinitely. This can lead to wasted resources, high costs, and difficulties managing large volumes of data. Instead, it is essential to establish retention policies that determine how long emails should be kept based on regulations and business needs.
- Email archiving equals backup: Some people confuse email archiving with traditional backups. Although both practices are important, they serve different purposes. Email archiving focuses on long-term data storage, while backups are for quick data recovery in case of loss or system failure.
- Email archiving is the sole responsibility of the IT department: Email archiving is an organization-wide responsibility. All departments must be aware of the archiving policies that apply to their area and comply with the established guidelines. In addition, compliance, legal, and human resources teams must also be involved in defining policies and properly managing email archiving.
Takeaways
In summary, the management of electronic communications is a complex but essential task for financial institutions in the digital age. Through a combination of message auditing, brand governance, regulatory compliance, and email archiving, financial institutions can successfully navigate the digital landscape, protect their reputations, improve customer experience, and stay on the right side of business. the law.