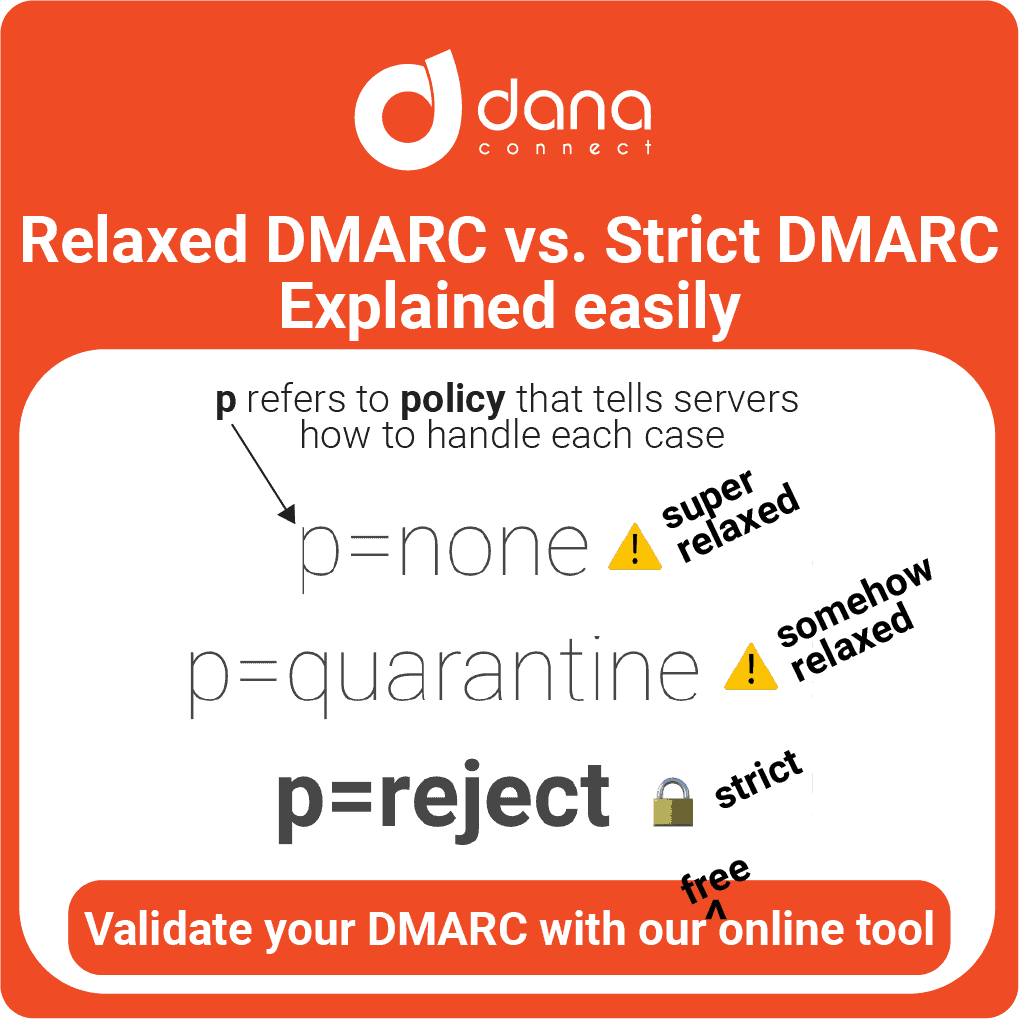
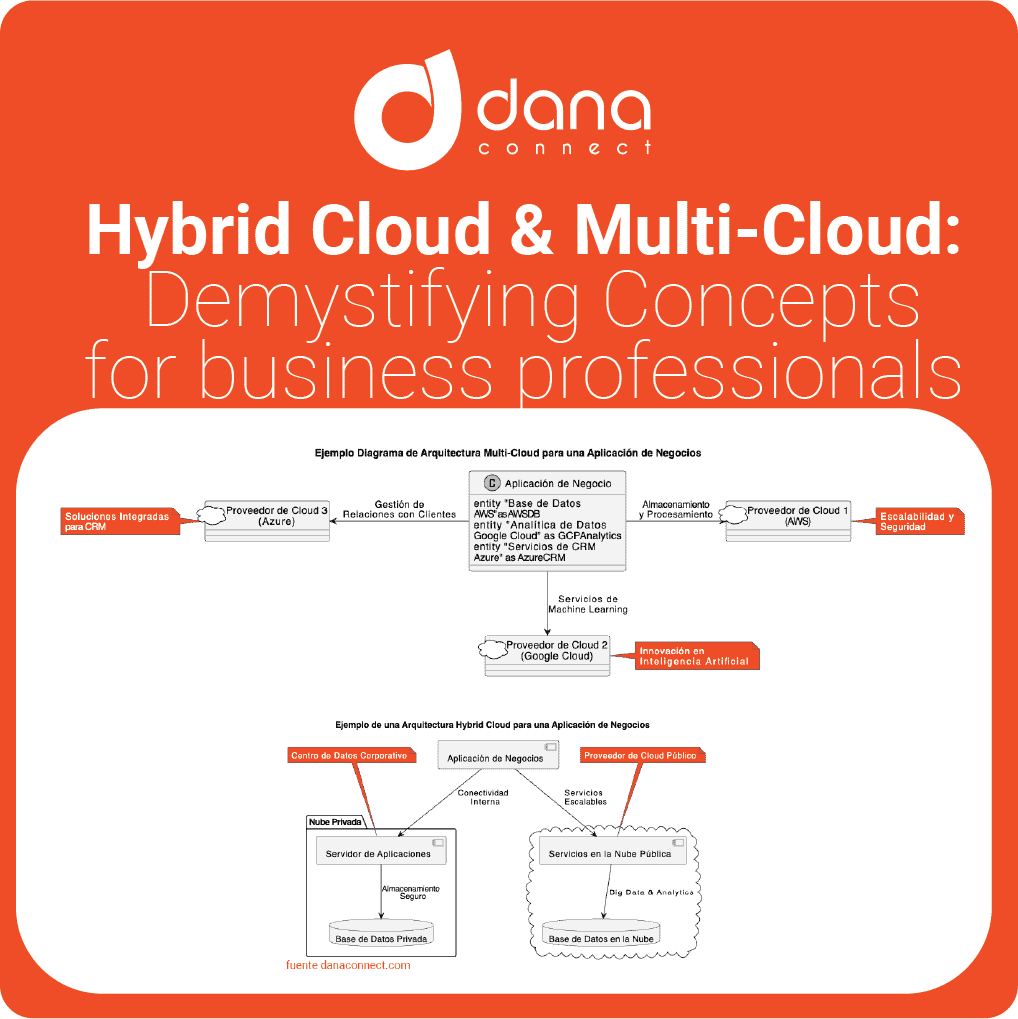
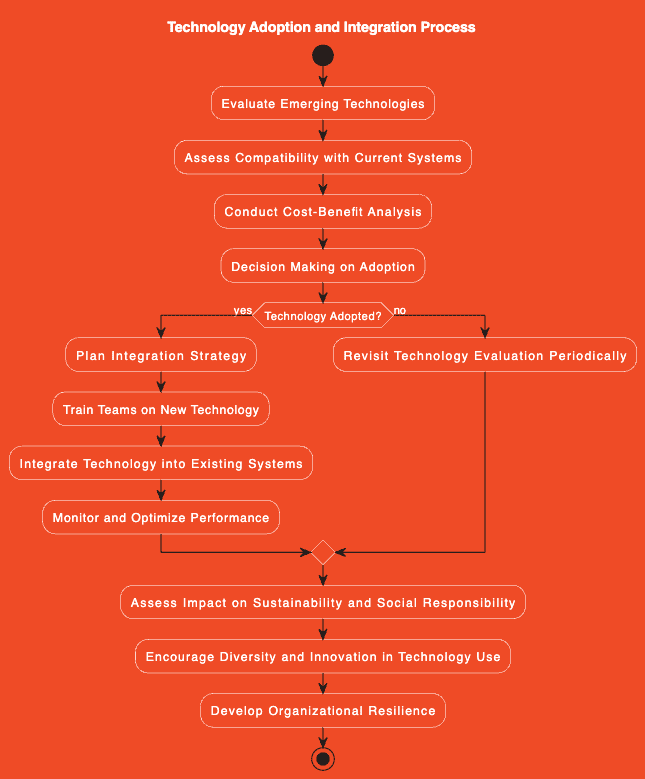
In today’s digital world, it’s important to understand the terms and language used to describe the various aspects of the digital realm. This article provides a curated glossary of digital terms to help you understand the lingo of the digital world from AI to UX. With easy-to-understand definitions and examples, this guide will provide a valuable reference for industry leaders looking to become more informed in the digital space. We will be adding more terms progressively as they appear.
AI:
A.I. stands for Artificial Intelligence. It refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. A.I. technology is used to develop computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as recognizing speech, making decisions, and understanding natural language.
There are different types of A.I., such as:
- Reactive Machines: they can only react to the current situation, they can’t use past experiences to inform current decisions.
- Limited Memory: they are able to use past experiences to inform current decisions.
- Theory of Mind: they understand the emotions, intentions, and beliefs of others.
- Self-Aware: they have consciousness and self-awareness.
A.I. can be used in a wide variety of applications, such as image recognition, natural language processing, robotics, and autonomous systems, as well as in fields like healthcare, finance, transportation, and more. It has the potential to revolutionize many aspects of our lives, but also raises concerns about the impact on society and the workforce, as well as ethical and safety issues.
A.I., Generative A.I.:
Generative artificial intelligence refers to a type of machine learning that involves training models to generate new examples of data, such as images, text, or music. These models are typically trained on large sets of existing data and can then be used to create new examples that are similar to the data they were trained on, but not identical.
API:
API stands for Application Programming Interface. It is a set of rules and protocols that allows different software systems to communicate with each other. Essentially, an API allows one piece of software to access the functionality of another piece of software, without having to know how it is implemented. This enables developers to easily integrate different systems and services into their own applications.
 API Economy:
API Economy:
API Economy refers to the use of APIs to easily share data with partners, quickly and easily integrating new products and services, and creating new revenue streams through the sale of data.
API economy refers to the use of Application Programming Interfaces to connect different systems and platforms, enabling the sharing of data and functionality. This term encompasses a wide range of innovative technologies and business models, such as the use of APIs to connect with external partners, fintechs, insurtechs, and other third parties. In the insurance industry, API economy allows companies to easily share data with partners, quickly and easily integrating new products and services, and creating new revenue streams through the sale of data.
As the insurance industry is increasingly impacted by digitalization and the use of technology, understanding the concept and implications of API economy can be very useful for business development professionals.
Read the article: What are the effects of the so-called API Economy on the financial industry
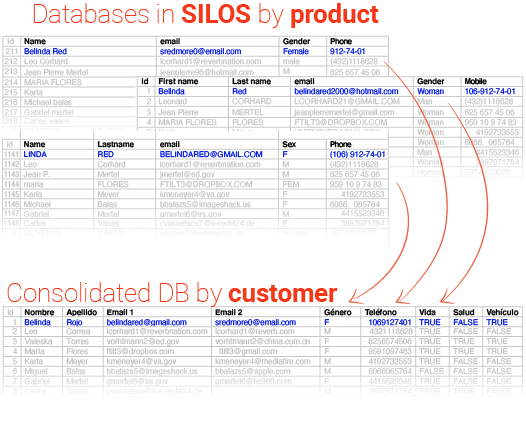
Big Data:
Big Data refers to the large volume of structured and unstructured data that is generated and collected at a rapid pace. This data can come from a variety of sources, such as social media, sensor data, and transactional systems. The sheer size and complexity of this data makes it difficult to process and analyze using traditional methods, hence the need for specialized technologies and techniques. The goal of Big Data is to extract valuable insights and knowledge from this data to make better decisions, improve operations and develop new products and services.
Blockchain:
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger technology that is used to record and verify transactions across a network of computers. It is the technology that underpins cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, but it has many other potential uses beyond digital currencies.
A blockchain is made up of a series of blocks that contain information about transactions. Each block is linked to the one before it, creating a chain of blocks, hence the name blockchain. Once a block is added to the chain, the information it contains cannot be altered or deleted, making the blockchain a secure and tamper-proof way of recording data.
One of the most important features of blockchain technology is that it is a distributed system, which means that there is no central authority controlling it. Instead, the network is maintained by a network of users, or nodes, who work together to validate and record transactions. This decentralized architecture makes it very difficult for any one party to manipulate or corrupt the data on the blockchain.
Blockchain technology has many potential use cases across different industries such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, and many more.
Business-Led IT:
Business-Led IT refers to any technology that is purchased and used outside of the IT department or outside of the CIO’s purview.
In the past, this was known as shadowIT, which the IT department considered a security concern and could lead to data silos and security concerns. In recent years, however, shadow IT or as it is better called now, “business-led IT”, has gained a reputation as a method of increasing productivity and efficiency within companies and a driver of innovation.
Business leaders are increasingly involving IT departments in their decisions regarding tools and technology to increase productivity, and to better understand how the software could benefit the organization as a whole.
It is critical for productivity that the IT department work in partnership with business users to achieve business-led IT.
Business Technologist:
Business Technologist is an employee who reports outside of IT departments and creates technology or analytics capabilities for internal or external business use.
A business technologist is someone who is responsible for creating, managing, and implementing technology solutions that are tailored to the needs of an organization. Business technologists must possess a range of technical and business skills, including knowledge of computer systems, networking, software development, project management, and business principles. They also need to be able to communicate effectively with various stakeholders in order to understand and meet organizational objectives.
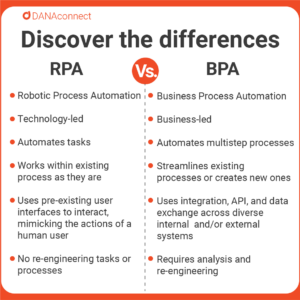 Business Process Automation:
Business Process Automation:
Business process automation (BPA) refers to the use of software to automate one or more business processes.
Most organizations use BPA to optimize their operating models, improve customer experience, increase employee productivity, and reduce costs. BPA can be implemented through software or a combination of software, infrastructure, and business rules. The best way to understand what BPA is is to look at its components and how they fit together.
Read the article: “Business Process Automation versus Robotic Process Automation: What is the difference?”
ChatGPT
ChatGPT, GPT-3 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3), is a state-of-the-art language generation model developed by OpenAI. It uses deep learning techniques to generate human-like text. GPT-3 is trained on a massive amount of text data, and it can generate text in a variety of styles and formats, including news articles, stories, poems, and more. GPT-3 can also be fine-tuned on specific tasks, such as answering questions, translating languages, and summarizing text. It is one of the largest models of its kind with 175 billion parameters, which allows it to generate text that is often indistinguishable from text written by a human.
Read the article: How to Leverage Virtual Assistants with Conversational Intelligence to Improve Customer Satisfaction / CSAT
Citizen Developer:
Citizen Developers are non-IT-trained employees who create new business applications using low code development platforms.
A citizen developer creates application capabilities for consumption by themselves or others, using tools that are not actively forbidden or o actually approved by IT. A citizen developer is a persona, not a title or targeted role. They report to a business unit or function other than IT. All citizen developers are business technologists. However, all business technologists are not necessarily citizen developers. There is no required designation of proficiency or time allocation for citizen developers but they must be legal employees of an organization.
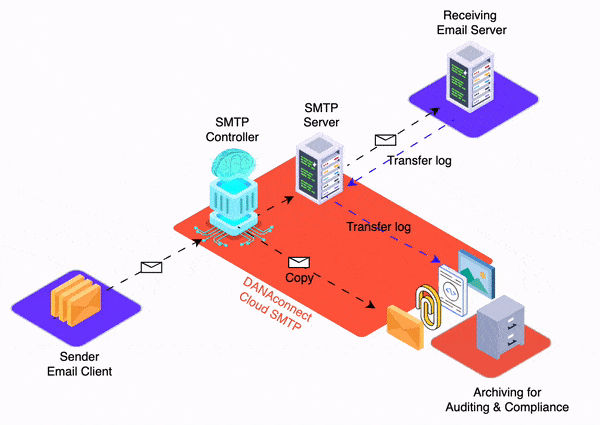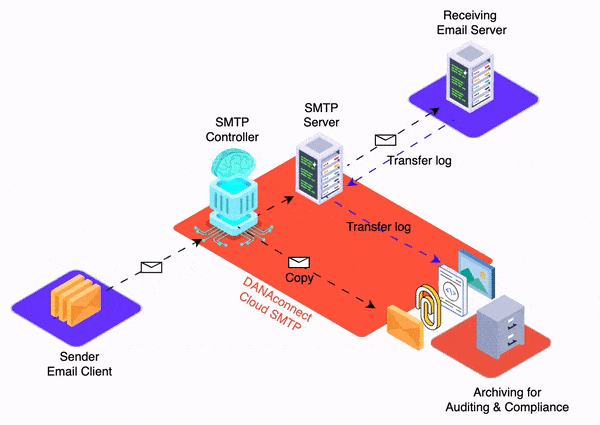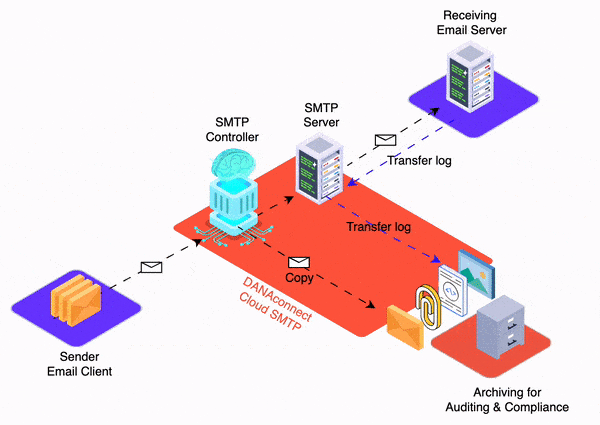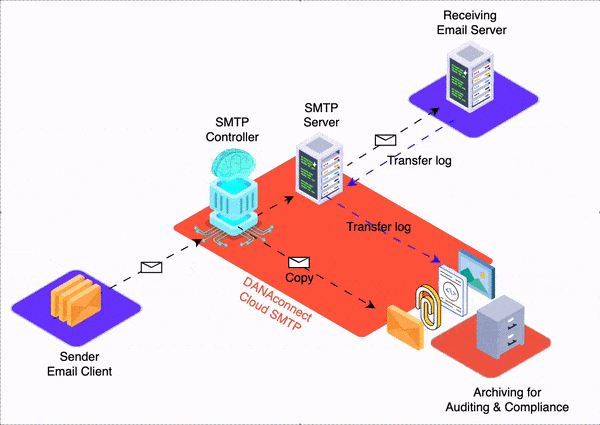
For example DANAconnect´s users are usually citizen developers as they don’t need to know technical stuff to create automation workflows.
Cross-channel:
Cross-channel refers to the ability of a company or organization to communicate or interact with customers using multiple channels, such as in-store, online, mobile, social media, email, and more. It is a communication strategy that allows companies to reach customers through different channels and touchpoints, and to provide a consistent message and experience across all of them.
A cross-channel strategy is designed to provide customers with a seamless experience across different touchpoints, allowing them to start a task or purchase on one channel and complete it on another, while keeping track of their interactions and preferences. This includes making sure that customer information and purchase history is available across all channels.
Cross-channel marketing also allows businesses to collect data and insights from various touchpoints to create a holistic view of the customer, which can help personalize interactions and improve customer satisfaction.
It’s a way for companies to be present and available for customers at every step of their buying journey, creating a seamless experience that leads to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and sales.
Read the article: Single-channel, Multi-channel, Omni-channel or Cross-channel? What is the best strategy?
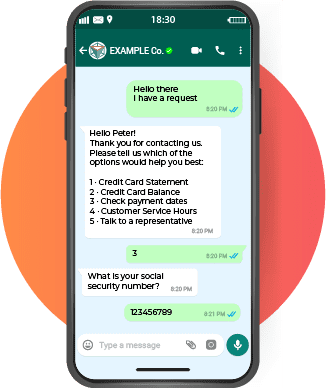
Conversational A.I.
Conversational A.I. refers to the use of artificial intelligence to enable natural and human-like communication between humans and computers.
Conversational A.I. involves technologies such as chatbots and virtual assistants that can understand and respond to customer inquiries and requests in a conversational manner. In the financial industry, conversational AI can be used to improve customer engagement and service, such as by providing instant assistance and answering frequently asked questions, as well as to automate sales and marketing tasks.
As the use of chatbots, voice assistants, and messaging platforms increase in the insurance industry and banking industry, understanding the concept and implications of conversational AI can be very useful for professionals in the sector.
For example you can use DANAconnect to create chatbots with conversational A.I.
Read the article: How to Leverage Virtual Assistants with Conversational Intelligence to Improve Customer Satisfaction / CSAT
Customer-centric:
Being customer-centric means putting the needs and wants of customers at the center of a company’s decision-making and operations. A customer-centric approach focuses on creating a positive and personalized experience for customers throughout their journey with a company.
Adopting a customer-centric approach requires understanding customer needs and preferences, and designing and delivering products, services, and interactions that meet or exceed those needs. It also requires a company-wide commitment to customer satisfaction, as well as an understanding that customer feedback and input are essential for continuous improvement.
In order to be customer-centric, companies should focus on gathering customer feedback regularly, and use data and insights to inform decision-making and product development. They should also empower employees to make decisions that benefit customers, and create a culture that encourages customer-centric thinking.
Customer-centric companies tend to have a loyal and satisfied customer base, and in the long run, achieve better financial results.
Read the article related to customer-centric: What do successful companies do differently to improve their customer experience?
CX:
Customer experience (CX) refers to the overall perception that customers have of a company and its products or services. It encompasses all aspects of the customer’s interaction with the company, including pre-sales activities (such as researching a product or service), the actual purchase and use of the product or service, and post-sales activities (such as customer service and support).
CX is becoming increasingly important as customers have more choices and companies are looking for ways to differentiate themselves. A positive customer experience can lead to increased customer loyalty and advocacy, while a negative experience can lead to customers switching to competitors.
Creating a positive CX requires understanding customer needs and preferences, and designing and delivering products, services, and interactions that meet or exceed those needs. This can be achieved through various approaches like customer research, user experience design, and customer journey mapping. Companies also use technology such as analytics, automation, and AI to gain insights and improve CX.
Good CX is a continuous process of improvement, requires a holistic approach, and should be aligned with the company’s overall strategy and goals.
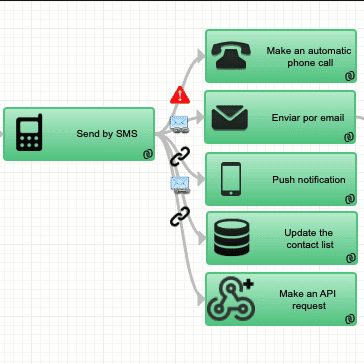
Decision Automation:
Decision Automation is the software that combines artificial intelligence, data, and business rules to assist businesses in making decisions in an automated fashion.
Decision Automation is a practice that utilizes multiple techniques and technologies such as AI/ML, Business Rules, Multistep decisions, Orchestration, Decision Robotics, etc. to automate decision-making processes across organizations. The automated decisions may go cross multiple organization boundaries, functional groups, departments, etc. to deliver higher business value and outcomes. Decision Automation enables organizations to automate the decision-making process in many different areas (i.e., within a process, application, department, etc.). There are many benefits to automating decisions, such as increased productivity, reduced risk and error rates, and increased consistency of decisions.
For example you can use DANAconnect to create decision automation workflows.
 Digital Maturity
Digital Maturity
Digital maturity refers to the level of advancement an organization has achieved in integrating digital technologies, processes, and data into its operations and strategy. It is often used to assess the level of digitalization and automation within a company, and how well it adapts to digital changes and challenges. A company with a high level of digital maturity is able to leverage technology to improve its efficiency, communication, and customer service, and is able to make data-driven decisions. It is able to understand the digital landscape and the opportunities it can bring, and to be agile in changing to adapt to the digital environment. The concept of digital maturity can be evaluated by several frameworks that assesses the digitalization of a company in various areas such as digital strategy, governance, and culture.
Read the article: The 4 stages of digital maturity
Digital Disruption:
Digital disruption refers to the significant changes and challenges that organizations face as a result of the rapid development and adoption of digital technologies. It is the process by which digital technologies and business models disrupt and transform existing markets and industries.
Digital disruption can come in many forms, such as new digital products or services that replace traditional ones, new business models that challenge existing ones, or new ways of delivering products or services that make existing ones obsolete. It can also come from the emergence of new digital competitors that are able to quickly gain market share by leveraging digital technologies and data in new ways.
The effects of digital disruption can be both positive and negative, it can create new opportunities for growth and innovation, but it can also make it harder for companies to stay competitive and relevant. Companies that are able to adapt to digital disruption by embracing new technologies, business models and ways of working, can gain a significant competitive advantage.
Digital disruption is a global trend and it has affected a wide range of industries, from retail and transportation to healthcare, insurance and banking. It’s important for organizations to be aware of the potential for digital disruption and to develop strategies to address it, such as embracing digital technologies, innovation and data-driven decision making.
Read the article : The painful IT Architect’s dilema of embracing disruptive technologies while still dealing with legacy systems
Digital Trust:
Digital trust refers to the level of confidence and belief that individuals, organizations, and society have in the security, reliability, and integrity of digital systems and the information they contain. It encompasses the trust that users have in the technology itself, as well as the trust in the organizations and individuals who provide and manage it.
The importance of Digital trust lies in the fact that helps individuals and organizations feel secure in their use of digital technologies, and that they can rely on the information they receive from digital systems. It is also important for organizations to establish digital trust with their customers, as it can help to build stronger relationships and increase customer loyalty.
Read the articles:
Adoption of financial self-services grows in tandem with digital trust
A Communication Strategy to Build Trust in Your SMS Channel
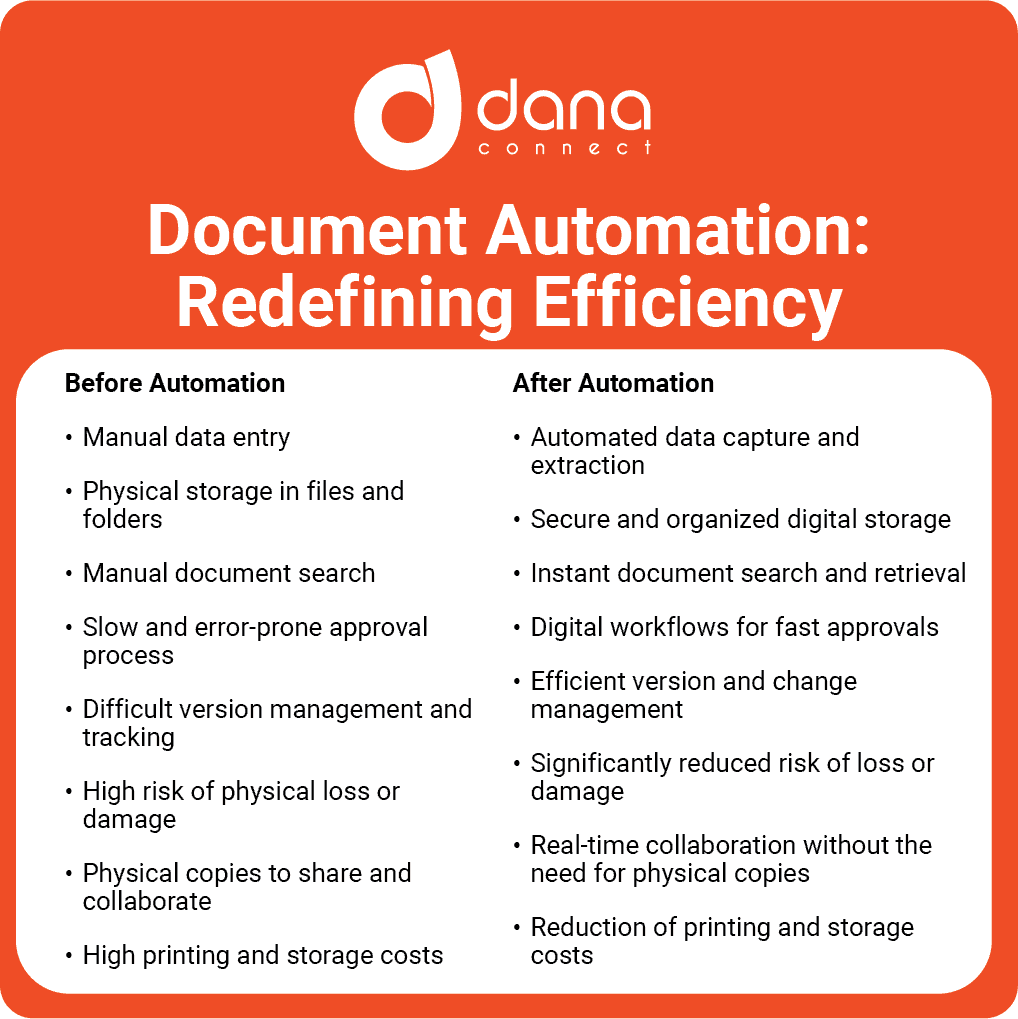
Document Generation Software:
Document generation software is a type of software that automates the process of creating, generating, and populating documents with data.
Document generation software can include a wide range of document types such as contracts, invoices, reports, and forms. The software typically uses templates to create documents, and allows users to input and manage data, such as customer information, product details, and financial data. Document generation software can be used to increase productivity and efficiency, by automating repetitive tasks and reducing the need for manual data entry, and can also be integrated with other software such as Insurance or Banking Core and accounting systems to pull in data automatically.
Digital Immune System:
Digital Immune System is an engineering strategy that integrates software to autonomously detect, mitigate, and respond to operational risks and security threats in real time.
A Digital Immune System, also known as DIS, monitors a company’s digital infrastructure, such as networks, devices, and applications, and uses algorithms to analyze data and identify abnormal behavior that may indicate a cyber-attack.
It can also automatically respond to these threats by isolating affected devices and applications, quarantining malware, and alerting security teams to the issue. The goal of a DIS is to provide a proactive and adaptive defense against cyber threats, rather than relying solely on traditional, rule-based security systems that can be easily bypassed by sophisticated attackers.
Fintech:
Fintech is a term used to describe the use of technology to improve and innovate financial services.
The term fintech can include a wide range of services such as digital payments, digital banking, online lending, and personal financial management. Fintech companies typically use technology such as data analytics, mobile and web-based platforms, and digital tools to create new and more efficient financial products and services, and to reach and serve customers in new ways. Examples of fintech companies include online lenders, digital payment companies, and robo-advisors.
Insurtech:
Insurtech is a term used to describe the use of technology to innovate and improve the insurance industry.
The term insurtech can include the use of digital platforms, data analytics, and other technologies to make the process of buying, managing, and using insurance more efficient and convenient for customers. Examples include online insurance comparison sites, the use of telematics to track driving behavior and offer personalized car insurance rates, and the use of digital tools to streamline the claims process.
Low-code / No-code:
Low-code / No-code refers to developing applications on purely visual, intuitive interfaces with no need for programming experience.
Low-code/No-code platforms are software development tools that allow users to create and deploy applications without writing traditional programming code. These platforms use a visual, drag-and-drop interface, which makes it easier for non-technical users such as business analysts, process owners, and power users to create and customize applications.
Low-code platforms require a minimal amount of coding, while No-code platforms do not require any coding at all. This approach makes it possible to build, test, and deploy applications faster and at a lower cost, as it reduces the need for specialized development skills. These platforms are used in many different industries and business areas, such as workflows, process automation, data integration, and more.
For example DANAconnect is a low code / No-code platform.
Read the article: Low-code/no-code: transforms shadow IT problems into enterprise innovation
Natural Language Processing:
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a field of artificial intelligence and computational linguistics that focuses on the interactions between computers and human language. It aims to enable machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language in a way that is both natural and useful. NLP techniques are used to process and analyze large volumes of natural language data, such as text and speech, and are used in a wide range of applications, such as language translation, text summarization, sentiment analysis, question answering and many others. NLP is a subfield of AI that combines computer science, linguistics, and artificial intelligence.
Omni-channel:
Omnichannel refers to a multi-channel approach to sales, marketing and customer service that provides a seamless experience across all channels, whether it’s in-store, online, on mobile or via social media.
In terms of strategy, omnichannle allows customers to start a task or purchase on one channel and complete it on another, while keeping track of their interactions and preferences.
In practical terms, Omnichannel means providing a consistent and integrated experience for customers, regardless of how or where they choose to engage with a brand. This includes providing a consistent brand experience, as well as making sure that customer information and purchase history is available across all channels. This allows businesses to create a holistic view of the customer and personalize interactions, leading to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and sales.
Omnichannel is a way for companies to be present and available for customers at every step of their buying journey, creating a seamless experience that leads to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and sales.
Read the article: Single-channel, Multi-channel, Omni-channel or Cross-channel? What is the best strategy?
Phishing Attack
A phishing attack is a type of cybercrime in which a person or group poses as a legitimate entity in an electronic communication, such as an email or text message, in order to trick a victim into providing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial information. The goal of a phishing attack is typically to steal personal information or money from the victim. These attacks can also be used to spread malware or to gain access to a network for further attacks. It’s important to be aware of phishing tactics and to think twice before clicking on links or providing sensitive information in an email or message.
Read the article: Understanding Phishing Attacks: Spear Phishing, Whaling, Vishing, Spoofing, Smishing and How They Affect Your Brand Reputation
Phygital (digital + physical):
Phygital is a term that describes blending physical and digital experiences.
Phygital is a buzzword that was coined combining the words digital and physical to describe the merging of physical and digital experiences.
As a strategy, phygital involves constant evaluation, improvement and responding to the market as one organic organization. In order to become phygital, the processes, objectives, roles, and responsibilities require an omnichannel approach. There should be no competition between channels, but rather a balanced mix to create a seamless cross-channel experience.
Robotic Process Automation:
Robotic process automation (RPA) refers to the use of software to automate one or more business processes using software robotic agents to interact with and manipulate software.
RPA software robotic agents are programmed to perform the same tasks that a human would do in a predefined user interface. They are designed to follow a predefined set of instructions and usually repeat these actions at scale. Robotic process automation is most commonly used in back-end operations and can be applied to a wide range of industries and business functions.
Read the article: “Business Process Automation versus Robotic Process Automation: What is the difference?”
Shadow IT:
Shadow IT is the use of IT systems, software and services in an organization that are not managed, approved or supported by the organization’s information technology (IT) department. These systems and services can include cloud services, mobile devices, applications, and other IT solutions, typically created and maintained by employees. Shadow IT can cause security, compliance and data governance risks for organizations, as they are often not monitored or secured by the IT department.
Read the article: Low-code/no-code: transforms shadow IT problems into enterprise innovation
Unicorn:
A “unicorn” in the digital business world refers to a start-up company that has a valuation of over $1 billion. The term is used to describe the rarity of such successful companies, similar to the mythical creature.
UX:
User experience (UX) refers to the quality of the user’s interaction with and perceptions of a system. User experience design requires a deep understanding of the end-user’s needs, wants, and limitations. It involves the design of the entire process of acquiring and integrating the product, including aspects of branding, design, usability, and function. UX design is the process of understanding user behavior and creating products that provide meaningful and relevant experiences to users.