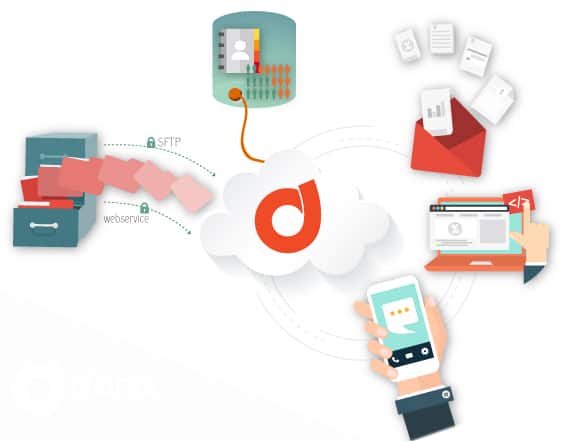
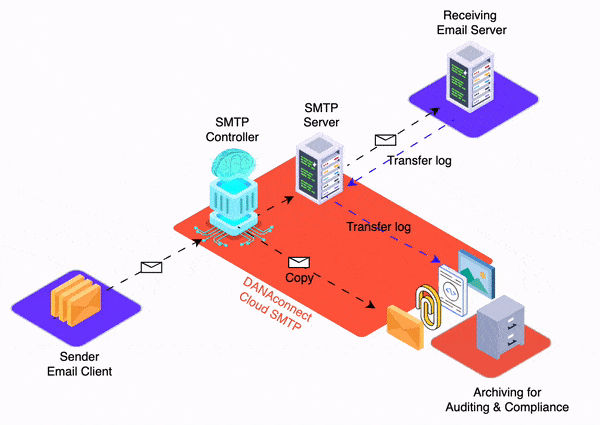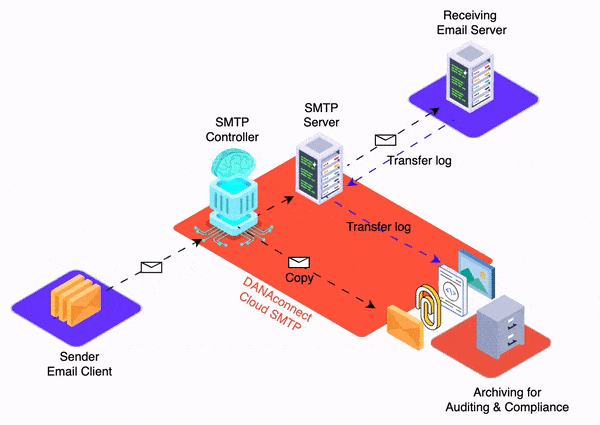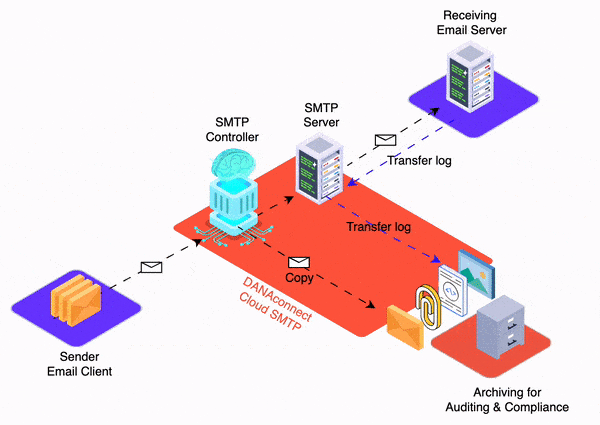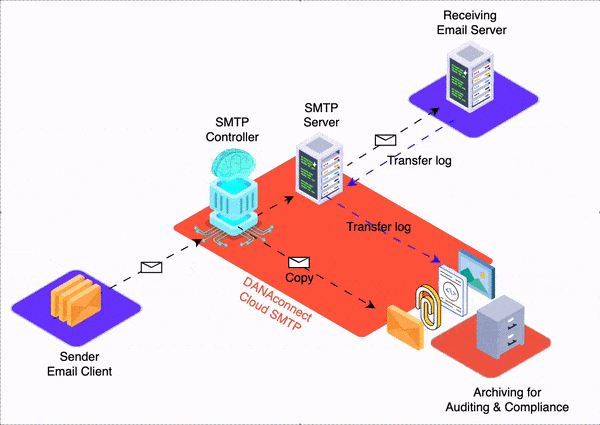
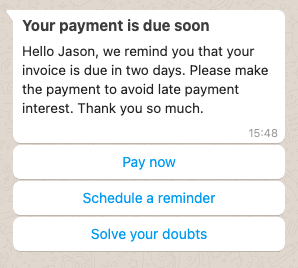
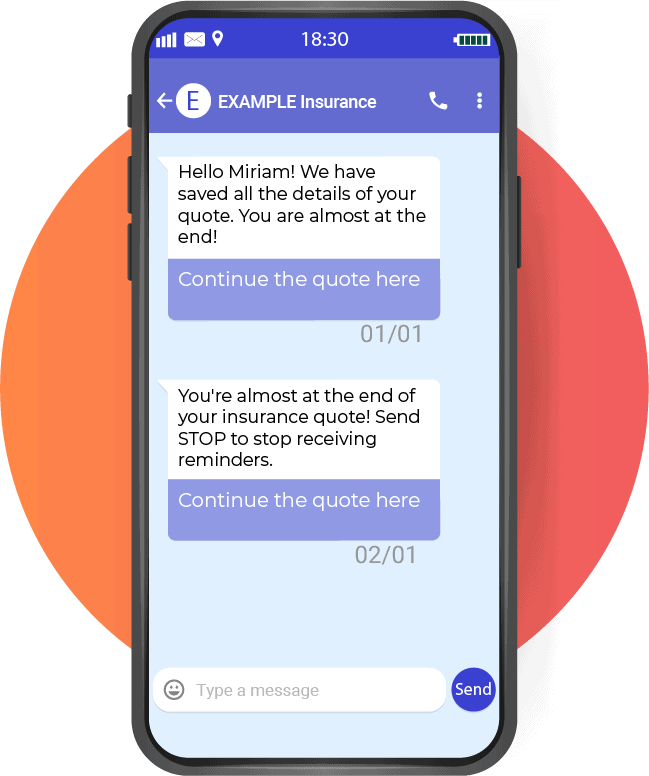
Having the infrastructure to send bulk email, such as marketing campaigns, collections or alerts, is the simplest part. If corporate email goes to spam this can pose a greater challenge, with severe consequences.
This especially true when we are talking about notifications, security alerts or have any critical document attached that have to comply with regulations, like invoices, account statements, insurance policies, electronically signed contracts, etc.
The problem of not reaching the inbox has as its source the amount of SPAM that is sent around the world. Currently, about 45% of the emails sent globally are actually SPAM, and consequently a lot of technology has been developed to filter them. As a consequence, when legitimate bulk emails are sent, it tends to be a great challenge to go through the controls that prevent spam from being delivered.
The 6 Worst Reasons Your Corporate Email Goes to Spam:
- The content of your email generates a high spam score
- Bad reputation of IP addresses
- Bad domain name reputation
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is misconfigured
- The SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is incorrectly configured
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) policies are wrong for your organization
How to solve the issue that your corporate Email Goes to Spam
The following 6 factors are most influential so your emails arrive at the inbox:
1. The content of your email generates a high spam score
More than 100 variables are analyzed within the content of an email for detecting if it is spam. The top 6 ones are:
- Image/text ratio. An email with only images and without text in the body of the email, it is interpreted as an attempt to hide the content to be delivered.
- Use of similar words for products that are prohibited from being sold on the Internet.
- Reputation of the domains of the links to which the email points to.
- Content of attachments.
- Broken links in emails.
- Use of Javascript.
Watch this tutorial:
DANAconnect Academy: How to check Email Spam Score
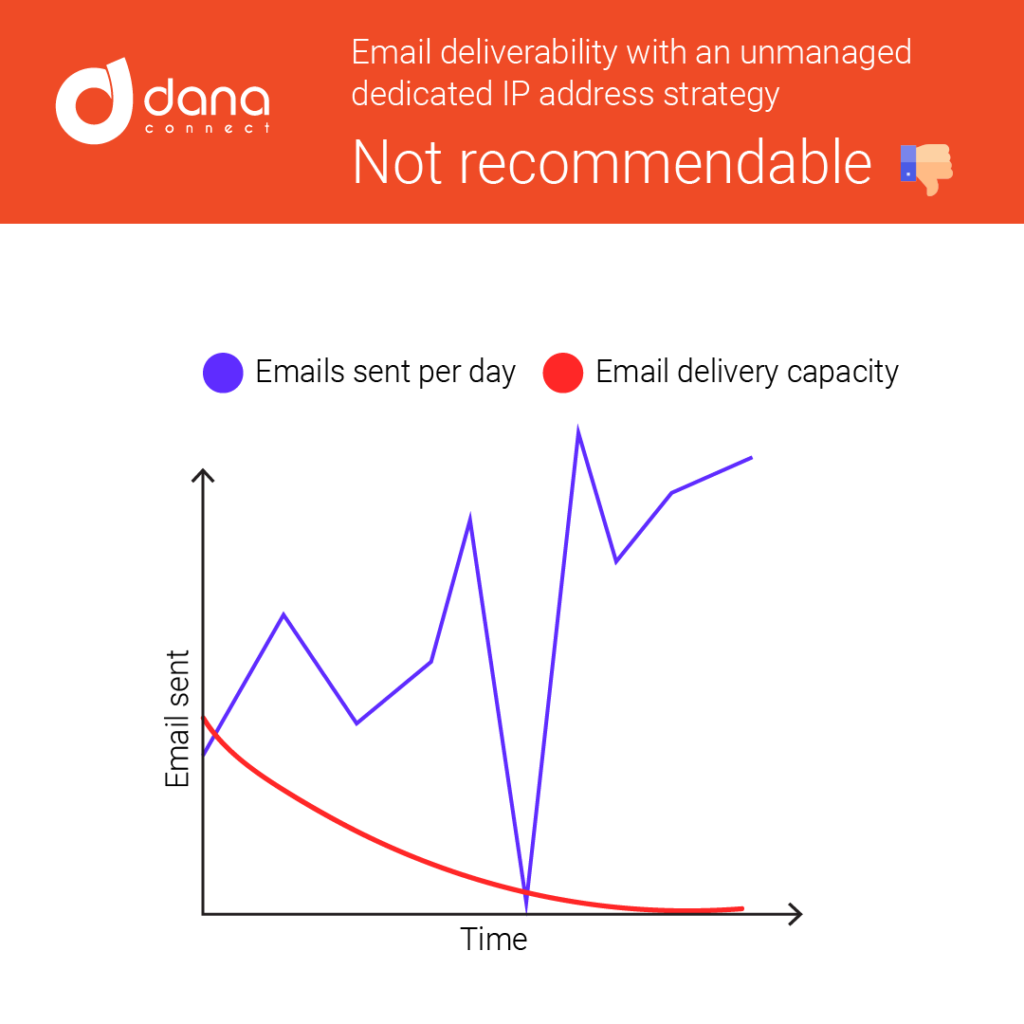
2. Sender IP address reputation:
The IP addresses from which emails are sent play a very important role in getting emails delivered to the inbox.
If an IP address has a low score, is not reputable, or is on multiple blacklists, the email may be rejected entirely.
The main reasons why an IP address has a bad reputation:
- Sending emails from that IP to mailboxes that do not exist.
- SPAM complaints for emails sent from that IP.
- Sending emails to SPAMTraps
What are Spamtraps?
Spamtraps are email address secretly created by Internet Service providers (ISP), like Google or Yahoo, to catch spammers.
3. Reputation of the domain name:
If a domain name appears on a blacklist or there is an alert that it is infected with malware, then it is quite certain that the emails will be completely rejected.
4. DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) configuration:
This mechanism allows an organization to take responsibility for sending a message, so that it can be validated by a recipient.
DKIM also protects against email tampering, providing end-to-end integrity, from a signing module to a validator module.
In most cases, the signatory module acts on behalf of the originating organization by inserting a DKIM signature in the message headers, and the verification module on behalf of the recipient’s organization, validating the signature by obtaining the signer’s public key through DNS.
5. Correct configuration of the SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
The Sender Policy Framework is a technique that allows identifying the IP addresses authorized to send emails on behalf of a domain, through a record in the DNS.
The SPF is currently used in many organizations in order to make their communications more secure and reliable, since it makes identity theft difficult.
Passing the SPF validation considerably helps the emails to be delivered to the inbox.
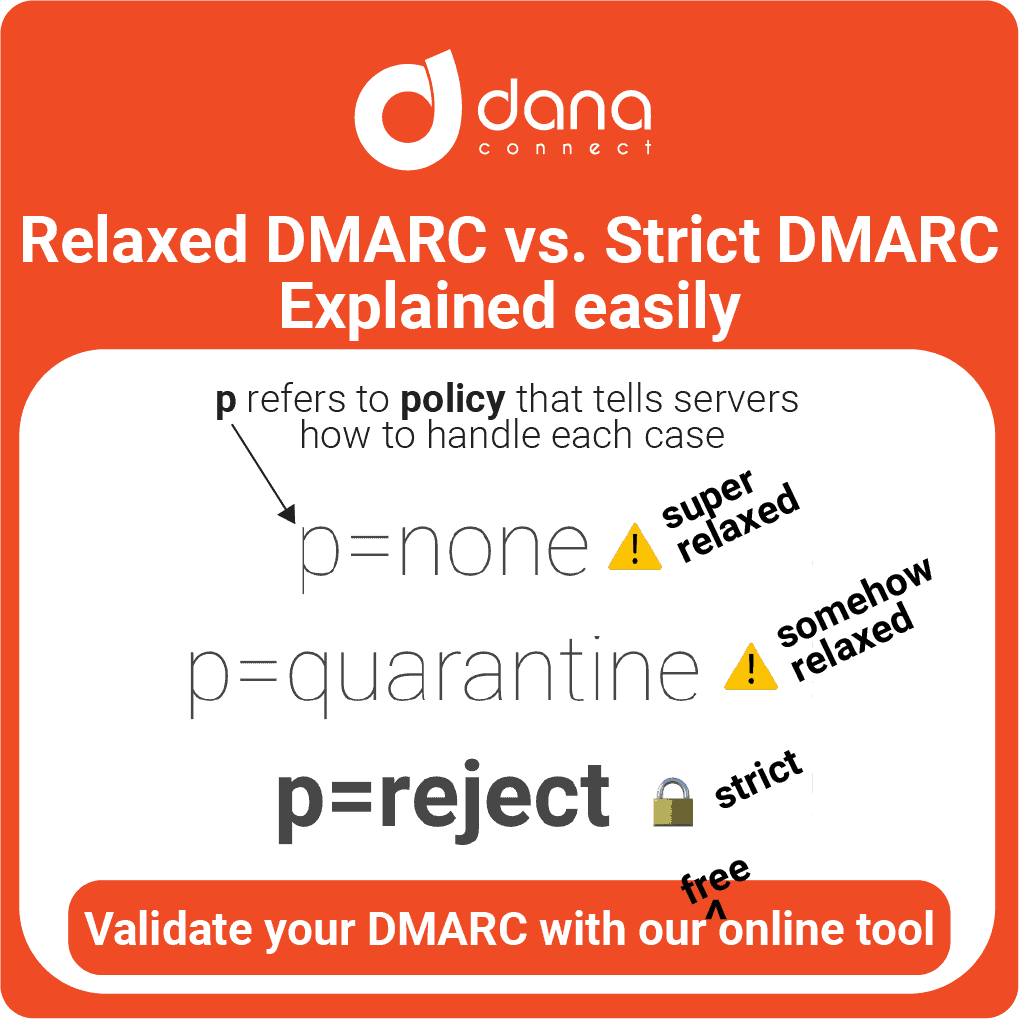
6. DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) configuration:
DMARC is an email authentication technique created to prevent third parties from sending unauthorized emails on behalf of a domain.
Setting up DMARC not only prevents phishing abuse or redirect attacks, it also helps improve the deliverability of legitimate emails to your inbox.
Successfully complying with these 6 factors makes the delivery rate to the inbox very high, thus allowing to keep an efficient communication through the email channel, which is very cost effective, rich in content and metrics.